Purpose
This article will provide an example of using opEvents to trigger opConfig to make an operational change.
Use Case
If an interface starts registering input errors, we want to automatically shift traffic off the circuit in order to maintain transmission quality.
Related Pages
Before attempting this configuration the admin should be familiar with the following wiki articles.
Sequence Overview
- NMIS polls a router with an SNMP query.
- The router returns an ‘interface input error’ counter value that has increased; thus triggering a pre-defined threshold.
- NMIS generates an ‘input error’ alert that is processed by opEvents.
- opEvents has a predefined action rule matching on node, interface and input errors. This action will fire an opConfig ‘Configuration Set’.
- The associated opConfig Configuration Set will increase the OSPF cost on the associated interfaces, thereby causing the router to select another path if available.
Configuration
NMIS
Be default NMIS has the necessary configuration for alerting on input errors. This is done with the NMIS thresholding system. The thresholds for the different alerting levels may be adjusted in the appropriate section of /usr/local/nmis8/models/Common-threshold.nmis. The levels below represent a percentage of input error packets as compared to good packets.
/usr/local/nmis8/models/Common-threshold.nmis
'pkt_errors_in' => {
opEvents
By default, opEvents processes the NMIS event log. All event are evaluated by /usr/local/omk/conf/EventActions.nmis. If an event matches a rule the appropriate actions will be taken. EventActions.nmis is also where we define the scripts that opEvents can fire. The first step is to define the scripts that will shift traffic off a link that’s running input errors. Since we want to shift all traffic off of this link we will need to run scrips for both ends of the circuit. Notice the reference to a configset; these will be defined in the opConfig section.
Changes to /usr/local/omk/conf/EventActions.nmis require that the omkd service be restarted.
/usr/local/omk/conf/EventActions.nmis
'script' => {
With the scripts defined let’s add the matching rule to the policy section.
/usr/local/omk/conf/EventActions.nmis
'policy' => {
opConfig
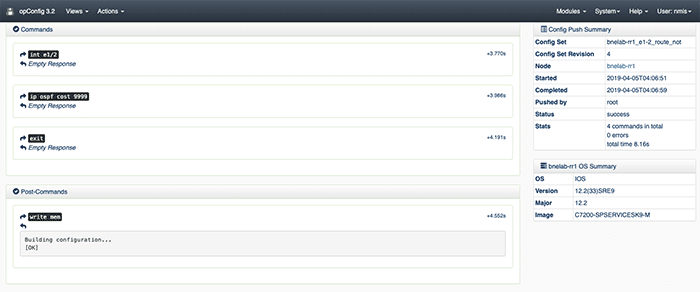
The next step is to define the config sets. Config sets are opConfig talk for the configuration commands you’d like to be run on the router. Because this step is complicated, yet very repeatable, I’ve supplied this script: writeConfigSet.sh. Run the script and it will prompt you for the commands you want to be run on the router and install the config set in opConfig. In order to verify config sets use the opConfig GUI, from the top menu bar select views, then Configuration Set Overview.
Here is what our example config set looks like.
{
Testing and Verification
Generate Input Errors
There are several different kinds of input errors but the easiest kind to create in a lab environment are giants. This is done by having mismatched MTU’s on either side of the same circuit; then sending packets that are too big from the side with the larger MTU.