
Getting Support at FirstWave – For Customers
Thank you for contacting Support at FirstWave.
For us to assist you in creating a case, you will need to:
For any assistance or inquiries, reach out to us at
support@firstwave.com.

Thank you for contacting Support at FirstWave.
For us to assist you in creating a case, you will need to:
For any assistance or inquiries, reach out to us at
support@firstwave.com.

As businesses increasingly rely on distributed systems and microservices to serve their growing networks, effective communication between their different components becomes more challenging.
Enter message bus, or enterprise service bus: a communication system enabling seamless data exchange between network components to help you manage your distributed network.
In this blog, we’ll break down the concept of a message bus architecture, explaining how it works, its core features, available alternatives, and the benefits that a message bus solution like FirstWave opHA-MB brings to distributed systems.
Imagine a bustling city with numerous neighborhoods, each representing a different application or service. To keep the city running smoothly, these neighborhoods need to exchange information efficiently.
A message bus acts like the city’s central transit system, ensuring messages are delivered to the right destinations without requiring any direct connections between them. In technical terms, the message bus enables different applications, services, or systems to communicate by transmitting messages through a shared infrastructure.
This setup ensures that each component remains independent for flexibility and scalability.
1. Producers (pollers)
Also known as peers, pollers collect data from various network devices and systems, generating messages that contain critical information about network performance, events, and statuses. These pollers can be scaled horizontally or vertically for efficient data collection across expansive networks.
2. Broker (message bus)
Serving as the central communication hub, the message bus ensures real-time synchronization among multiple pollers. It manages the routing of messages from producers to consumers, maintaining data integrity through message replication across three nodes, which allows the system to tolerate single-node failures.
3. Consumers (primary server and applications)
The primary server and associated applications function as consumers. They receive and process messages relayed by the message bus, providing users with a consolidated, real-time view of network health and performance. This setup enhances capabilities like event logging, monitoring, and the generation of intuitive dashboards and reports.
A message bus decouples communication, instead allowing senders and receivers to operate independently so network communication can happen asynchronously. This means users can manage distributed network systems via a central point that standardizes disparate communication styles. The result: a simple, integrated system.
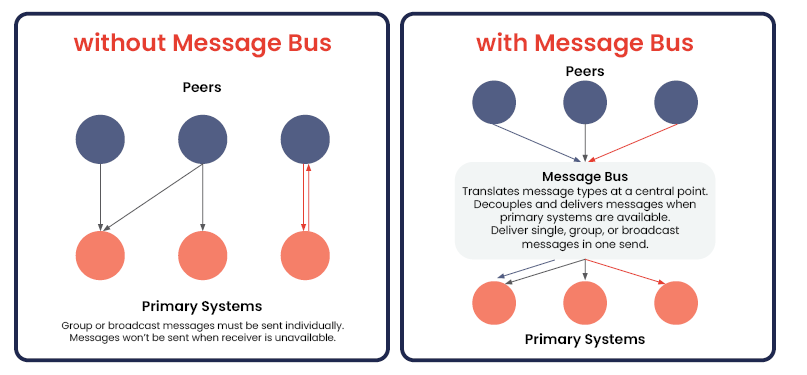
A message bus architecture is useful for businesses managing large-scale, distributed, multi-customer, and/or mission-critical networks, as data is freely available to travel between endpoints as needed.
In modern network management and cybersecurity environments, different services handle distinct functions—such as network monitoring, security alerts, performance analytics, and automation workflows—while seamlessly communicating with each other. A good message bus acts as the backbone for this communication, ensuring that services remain loosely coupled, scalable, and resilient in distributed architectures.
Network management benefits for microservices include:
Modern applications rely on real-time event processing to improve responsiveness and automation. A message bus is a core component of event-driven architectures, where events (e.g., user actions, system changes, external triggers) are published and consumed dynamically.
Where it’s useful:
Alternatives to a message bus are usually point-to-point based, where services communicate directly rather than via a central interconnected point.
Point-to-point communication has its benefits, but it does limit your capabilities in that it silos data between sender and receiver, preventing cross-communication which can limit efficiency in more complex architectures.
But the good news is that you’re not just limited to one option; your distributed system can use a combination of communication styles for different functions to optimize its efficiency for your business.
APIs are a tightly coupled solution where each of your services need to know about each of your endpoints. With APIs, each service manages its own connections. This approach is ideal for simpler architectures or where latency isn’t a major consideration.
Pros:
Cons:
A message queue is similar to a message bus, but they differ in how messages are routed and processed. Unlike a message bus, a message queue uses point-to-point communication and messages are prioritized by first in, first out. Once consumed, the message is simply removed from the queue.
Pros:
Cons:
If you have the time to implement and manage them all efficiently, you can use a message bus alongside other communication methods to expand your feature scope and optimize your setup for different use cases.
Some single providers will provide all of these functionalities in-house to make your journey even easier; for example, in addition to FirstWave’s opHA Message Bus solution, we also provide APIs to allow for message transfers, as well as integrate with queue-based message brokers such as RabbitMQ – all combined with hands-on expert support to make implementation easy.
To help you choose the best design (or combination of designs) for your business, ask yourself the following questions:
opHA Message Bus (opHA-MB) is FirstWave’s own message bus solution, enabling you to simplify management of your distributed network systems with real-time data transfer across diverse and multi-tenanted environments.
This advanced network management solution acts as the central nervous system to your network to help you maintain optimal network performance, ensure resilience, and swiftly resolve the issues that come with complex network infrastructure.
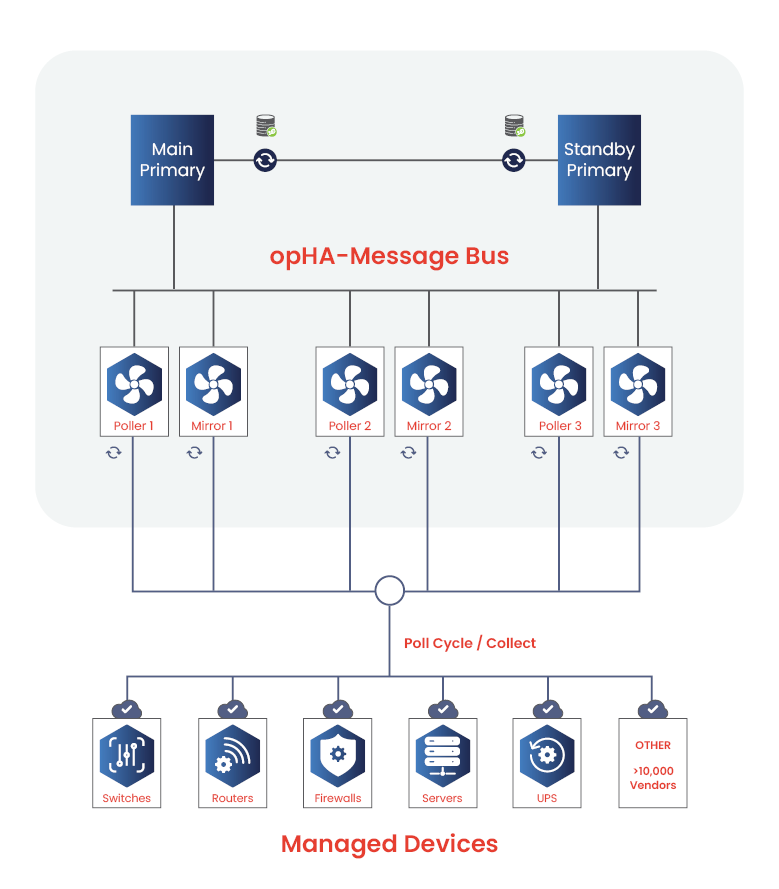
By keeping producers and consumers decoupled, this architecture allows each component to function independently. This improves flexibility, scalability, and resilience—ensuring efficient network management even as demands grow.
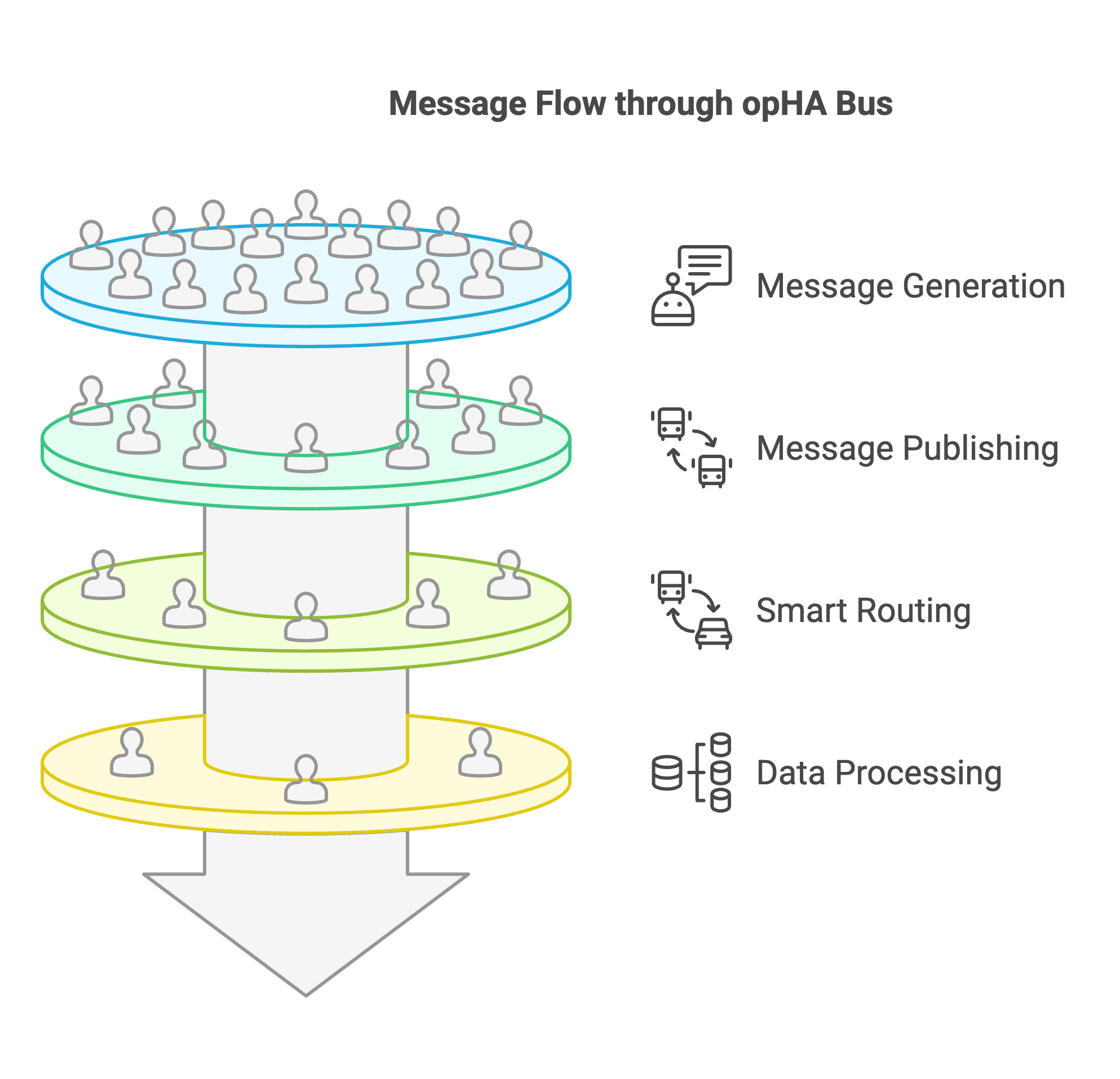

By activating the Virtual Operator feature in the NMIS opConfig module, IT managers can empower their team to proactively address common network issues, ensuring optimal performance, security, and compliance.
The virtual operator can:

The Evolution of Network Operations – from Manual to Virtual
The landscape of network operations has been undergoing a radical transformation.
Traditionally, managing networks involved a predominantly manual approach, relying heavily on human expertise and intervention to address issues, configure devices, and ensure optimal performance. Human error, time-consuming processes, and the inability to scale effectively in the face of growing network complexity posed significant challenges to traditional network management practices.
In the past decade, network monitoring and management platforms have become more intelligent, with advances in big data providing greater insights into a network environment, how and when it is accessed, what devices are used and when, which services are performing optimally, and which services are degrading.
According to the Gartner Market Guide to Network Automation, while more than 65% of enterprise networking activities are performed manually across SME’s, a growing percentage of large enterprises automate more than half of their network activities.
Firstwave Cloud Technology has been at the forefront of this new era of machine intelligence, gathering and analysing network data to provide advanced anomaly detection and predictive analytics that allows operators to proactively manage infrastructure and devices to ensure a healthy and predictable network environment.
With the introduction of the Virtual Operator, this machine intelligence goes a level deeper, allowing the NMIS platform to take action on insights and allowing operators to script a series of activities that the operator can perform at the touch of a button.
This article delves more deeply into the concept of the Virtual Operator, exploring its benefits and potential impact on an organisation’s network automation strategy. We will examine how automation, through the implementation of a Virtual Operator, is reimagining network administration, driving efficiency, enhancing security, and unlocking new levels of performance and insights.
What is the Virtual Operator?
The Virtual Operator, is a software agent designed to automate repetitive tasks, optimise network performance, and provide intelligent insights. It functions as a rule-based engine that learns from historical data, network configurations, and best practices, allowing it to make informed decisions and take proactive actions to maintain network stability and efficiency.
Think of a Virtual Operator as a highly specialised AI assistant tailored for network administration. It acts like an extension of the network team, taking on the mundane and repetitive tasks, freeing up human engineers to focus on more strategic and complex challenges.
Benefits of implementing a Virtual Operator
The implementation of a Virtual Operator offers several key benefits to network administration teams:
By automating routine tasks, the Virtual Operator can free up engineers to focus on more strategic and complex challenges. This shift allows teams to maximise human talent, enabling them to tackle innovation, problem-solving, and the implementation of new technologies.
The Virtual Operator in conjunction with the broader opConfig and opEvents module can continuously monitor network performance, identify potential issues, and proactively take corrective actions. This pre-emptive approach ensures optimal network performance, minimising downtime, and maximising resource utilisation.
The Virtual Operator can implement and enforce security policies, detect anomalies, and respond to security threats in real-time. This automated approach strengthens network security, improves compliance with industry regulations, and reduces the risk of security breaches.
Virtual Operators leverage vast amounts of network data to gain valuable insights and optimise network configurations. These insights empower network teams to make informed decisions based on real-time data, leading to more effective resource allocation and network optimisation.
Use Case: Managed Service Providers
Managed Service Providers (MSPs) often manage multiple client networks simultaneously. This can be a resource-intensive task, particularly when dealing with routine maintenance and troubleshooting. The Virtual Operator offers a solution to this challenge by automating many of the routine tasks that MSPs typically perform.
For example, a MSP can use the Virtual Operator to automate the process of applying security patches across multiple client networks. The Virtual Operator can execute the necessary commands to apply the patches, run tests to ensure that the patches have been applied correctly, and report any issues that arise. This not only reduces the workload for the MSP’s engineers but also ensures that the patches are applied consistently and without errors.
Use Case: Hybrid Networks
The Virtual Operator simplifies the management of hybrid networks by automating the tasks required to maintain connectivity and performance.
For example, the Virtual Operator can automatically adjust network configurations to optimise performance as workloads shift between on-premise and cloud environments. It can also monitor network traffic for potential issues and make adjustments in real-time to prevent disruptions. This level of automation ensures that hybrid networks operate smoothly and efficiently, even as conditions change .
How Businesses can expand their Network Automation beyond the Virtual Operator
The adoption of the Virtual Operator for network administration presents a key stepping stone towards the future of network automation for IT teams. How can a business expand the effectiveness of Virtual Operator and what new developments can we expect to see as network automation technology further evolves?
Use of the Virtual Operator alongside other modules such as opEvents, opTrend and Open-Audit will drive further automation in network management, eventually enabling self-healing networks that can identify and resolve issues without human intervention. This will lead to more resilient, reliable, and efficient network infrastructure.
The use of the Virtual Operator to routinely check network health will play a critical role in advancing network intelligence, enabling teams to gain deeper insights into network performance, security threats, and user behaviour. This will empower teams to make more informed decisions and proactively optimise their networks.
Eventually, the use of network automation tools such as the Virtual Operator will transform the role of network administrators and engineers, shifting their focus from routine tasks to more strategic and creative activities. They will become more involved in AI model development and instructional writing, data analysis, and the design of intelligent network solutions.
Conclusion
The Virtual Operator represents a significant step forward in network automation, leveraging the power of AI to enhance network performance, optimise operations, and free up human resources for more strategic tasks. As AI and automation continue to advance, features like the Virtual Operator will play an increasingly crucial role in enabling more intelligent, efficient, and resilient network infrastructure.
Reference:
Gartner 2023 Market Guide to Network Automation
https://www.gartner.com/en/documents/4913231

In a modern network environment, IT asset discovery is a must-have.
Having the ability to oversee and manage network devices helps you safeguard your data from unauthorised users, keep critical software and devices up-to-date, achieve compliance, and mitigate network threats. Plus, you’ll save valuable time and resources on network scanning and inventory management tasks.
Open-AudIT enables you to do all these things and more in real time – and you can have it completely up and running in under 10 minutes. We’ll show you how in this quick guide.
FirstWave’s open-source network discovery tool shows you what’s on your network, how it’s configured, and when it changes, so you can:
Open-AudIT does this by intelligently scanning your organization’s network and storing the configurations for the devices it discovers. This gives you immediate visibility into:
Open-AudIT can also collect huge amounts of data from varying networks, which can be catalogued and collated into meaningful reports. Not only is this tool free to download, we also offer a free 100-device Professional license to get you started.
The Open-AudIT installer will take care of most prerequisites for you, but make sure you have the following:
Operating system-specific prerequisites are also listed below. Learn more about the requirements for installing and running Open-AudIT here.
Visit our website to download the latest version. Select the Linux or Windows option, and download the binary.
Open-AudIT is installed on-premises. You can also use the FirstWave Virtual Machine if you prefer, and get all the FirstWave monitoring applications installed and ready to use.
Prerequisites
Installation
Get more info on installing and upgrading Open-AudIT for Windows.
Prerequisites
Installation
Get more info on installing and upgrading Open-AudIT for Linux.
Open-AudIT can handle a variety of credential types, including the standard SNMP, Windows, and SSH types.
If you don’t have the credentials for a device on your network you will still see the device in Open-AudIT, but data retrieval will be limited.
Now, you can add a discovery!
After adding your credentials and running your discoveries, you’ll notice your home dashboard now displays a variety of charts that give you deeper insights into your network.
Want a visual run-through? You can watch the entire process in more detail below.
Happy discovering!

In managing computer networks, keeping services running and minimizing disruptions is crucial. One important way to measure how well network managers and operators handle problems is through Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR).
MTTR is a key performance indicator used in network management to quantify the average time it takes to resolve a network issue or outage from the moment it is detected.
This metric encompasses the entire process, from initial problem identification (when a device such as a router, switch, or server goes down or starts experiencing issues) through to the restoration of normal service. MTTR is calculated by taking the total time spent on resolving all incidents within a specific period and dividing it by the number of incidents.

In simpler terms, MTTR provides a clear picture of how long your network is out of action during a typical incident and how quickly your team can bring everything back to normal. It’s a reflection of the efficiency and effectiveness of your incident response processes.
MTTR is more than a mere number; it serves as a direct indicator of the health of your network management practices. Here’s why it’s so crucial:
The definition of a “good” MTTR can vary depending on the industry, the complexity of the network, and the nature of the incidents. However, there are some general benchmarks that network managers can consider:
MTTR stands as a critical measure that network managers and operators need to monitor and improve. It acts as a clear signal of how rapidly your team can recover from network issues, affecting everything from operational efficiency to customer satisfaction. By aiming for a reduced MTTR, network teams are not only able to improve their service reliability but also bolster their overall network management approach. Ultimately, a successful MTTR is one that meets or surpasses your organization’s and its customers’ expectations, while continually striving for quicker and more effective resolutions.

Streamline your traffic management and boost your network efficiency with our easy step-by-step guide to using Secure Traffic Manager with NMIS.
In September 2023, FirstWave acquired a company called Saisei, including its flagship platform, Secure Traffic Manager (STM), for network traffic shaping and deep packet inspection.
This tool is a powerful way for telcos and large enterprises to monitor and manage network traffic, allowing certain applications or services to have greater Quality of Service (QoS) than others.
There are several benefits to using STM:
Using STM with FirstWave’s open-source network management solution, NMIS, gives you full visibility and control over this traffic so you can set rules to automate traffic management, orchestrate alerts, and more.
This quick guide’ll show you how to monitor your Saisei STM appliance with NMIS.
First, ensure that NMIS is installed and configured properly in your environment. Follow the installation instructions provided by FirstWave here. FirstWave offers a 20-node free license to get you started.
Enable SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) on your STM appliance. Configure SNMP settings such as community strings and SNMP versions according to your security policies and requirements.
In NMIS, add the STM appliance as a device to be monitored. You’ll need to provide the IP address or hostname of the STM appliance, SNMP community strings, and any other necessary authentication details.
Specify which parameters and metrics you want to monitor on the STM appliance. This could include things like bandwidth usage, network traffic, or CPU and memory utilization.
Define threshold levels for monitored parameters to trigger alerts when certain conditions are met. This allows you to proactively manage and respond to potential issues on the STM appliance.
Once configured, test your monitoring setup to ensure NMIS is successfully collecting data from the STM appliance and that alerts are working as expected.
Periodically review and update your monitoring configuration as needed. This ensures that your monitoring remains effective as your network and infrastructure evolve over time.
That’s it! Now you can get all the benefits of STM combined with all the benefits of NMIS. Throughout this process, you can refer to FirstWave documentation for specific guidance on integrating STM appliances with NMIS.
Need further assistance? Reach out to the FirstWave support team.