Ways You Can Manage Your IoT System Using Network Management Software
Table of Contents
- Internet of Things Systems and Applications
- IoT Use Cases
- Traditional Enterprise Applications
- IoT Applications
- Types of IoT Systems
- Monitoring IoT Systems
- Managing Things with NMIS
- Wrapping up
- Learn More
Internet of Things Systems and Applications
The use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is increasing, largely driven by the value seen by organizations in the application of these technologies to reduce costs, access more information, improve actionable insights, reduce downtime, improve customer experience, better manage risk, create new revenue streams, and much more. For many organizations, new applications of IoT are compelling; many organizations already use IoT and are looking to integrate IoT into their existing production network.
Enterprise Management Associates (EMA) research paper titled “Network Management Megatrends 2022: Navigating Multi-Cloud, IoT, and NetDevOps During a Labor Shortage, April 2022” indicated that of those organizations represented in the research, 96% were expecting to or were already connecting IoT devices to the corporate network. All the companies were making significant investments in networking and network monitoring technologies to handle increased demand for IoT.
For many people who have worked in IT, especially in networking for a while, IoT isn’t that new. The IP and storage networks, server clusters, mobile devices, etc., are smart devices that make data available to verify their operation. IT professionals have been using data to improve outcomes for decades.
However, IoT is a bit different. The use cases and IoT applications differ from traditional use cases and applications. Typically, IoT applications have a fundamentally different purpose and operate differently than traditional applications. The focus is on obtaining the necessary data and making it available for reporting, dashboards, real-time alerting, and longer-term analytics, including AI/ML.
IoT Use Cases
It’s virtually impossible to list all the types of IoT systems in use today, and new ones are emerging all the time. Manufacturing, logistics, retail, health, and many other sectors have been using IoT technologies for years. As sensors and networks become more robust and cheaper to produce and maintain, more use cases will arise. Here are some of the interesting ones encountered recently:
- Mine vehicle air quality
- Remote weather stations, including lightning strikes
- Soil moisture monitoring
- Livestock water trough monitors
- Moisture detection in buildings
Traditional Enterprise Applications
A traditional enterprise application would include a user accessing an application via their PC/mobile. This application likely has a frontend, application logic, and a database. It could be running on one or more servers or using microservices, containers, and databases. This could be a SaaS offering or could be hosted in the organization’s data center.
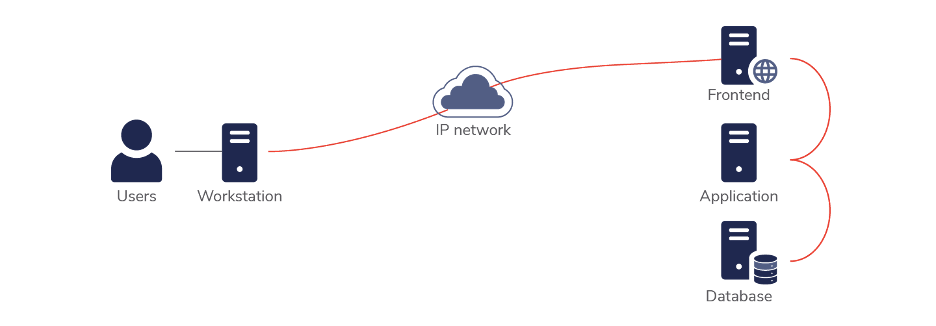
Typically, in an enterprise application, data is created by users (data entry). Users will also view the data for reporting, analysis, and to support business processes.
IoT Applications
In an IoT system, you’ll find collectors/sensors, the network/transport, and an application that processes all the data and provides a user interface for users to access the data.
The differences between a traditional and IoT application include:
- The network may not be end-to-end IP
- No data entry by users
In a non-IP IoT application, a device sends packets over a network to a backend application for processing. The network may NOT be IP. Communication is often one-way; polling devices isn’t possible. Eventually, packets are sent over IP and reach the servers used by the IoT application. Users aren’t involved in data entry; they access the IoT application for dashboards, analytics, etc.

Types of IoT Systems
Now that we’ve established we can monitor and manage an IoT system, how should we categorize them? The following are the main four types of IoT systems we see:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart IoT | Full stack OS with SNMP agent or native API and an IP address |
| IoT over IP | Semi-smart device hardwired to talk to Cloud Server |
| IoT over mobile | Roaming low power cellular devices using 3G/4G |
| IoT over low energy network | End devices use a low energy network (LoRaWAN, Bluetooth, Zigbee, etc.) to a gateway which then sends IP packets |
To collect data from an IoT System, we can further categorize how and where we’ll get the data. The following methods are possible:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Bi-directional comms | If the system uses Native IP, bi-directional communication with the end things is possible |
| Direct Polling | Direct communication with the end device is possible, at a minimum sending a protocol “ping”, e.g., ICMP packet |
| Application Polling | Determine the status of the end device and request metric data using a request or query to the application, e.g., an API request |
| Events or Messaging | The device communicates by sending events or messages, this could be syslog, streaming telemetry, MQTT, or another message bus. An intermediate gateway could translate messages into an IP packet |
Monitoring IoT Systems
We can now compare the types of IoT devices to the methods available to determine the best way to monitor the device:
| Name | Native IP | Bi-directional comms | Direct Polling | Application Polling | Events or Messaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart IoT | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | Yes |
| IoT over IP | Yes | No | No | Yes | Likely |
| IoT over mobile | No | No | No | Yes | Likely |
| IoT over low energy network | No | No | No | Yes | Likely |
This is a summary of how various IoT systems work, and there are many more variations, but most will fit this model. For example, many home IoT devices use IP but only communicate with the cloud application. It’s not possible to make local requests for data, while other home IoT devices support both.
The result is that NMIS can get data directly from the IoT device or from the IoT application, or it can listen for events using opEvents. If NMIS doesn’t already support your IoT application, it can be easily adapted using the modeling system and/or plugins.
Managing Things with NMIS
Now that we’ve identified the types of devices NMIS can manage, we can determine the best way to manage each of them in NMIS.
Smart IoT – Smart Cameras
Getting data from Smart IoT devices with NMIS is straightforward. The best option is to use SNMP to collect the data and have the device configured to send any SNMP traps and/or syslog to the NMIS server.
For example, while working with a large enterprise in the USA, the implementation team in the US assisted with the creation of an NMIS model that collected data from the Axis security cameras in use.
The focus of this work was to ensure all cameras were online and functioning. The goals for the IoT monitoring included:
- ICMP Ping to confirm reachability, packet loss, and response time of the devices
- sysUpTime poll to detect “Node Reboot”
- Current OS version
- Video Signal Status
- Traffic transmitted and received by the camera
- HTTP/HTTPS service/server operating and returning data
- Storage status (storage disruption detected)
- Temperature sensors
AXIS provides a public MIB file, which you can download here.
With access to a camera and the MIB file, it’s straightforward to complete the NMIS model and have NMIS collect this data.
Because of the proprietary nature of this work, these models haven’t been released publicly. If you’re interested in monitoring AXIS cameras, please contact the FirstWave team.
Monitoring Weather with IoT Over IP to the Cloud
IoT sensors provide many benefits by increasing available data and the amount of information and knowledge that can be derived. Monitoring the weather offers several advantages, including the ability to correlate weather events with network events. These events could be correlated by opEvents and provide the true root cause of outages.
Netatmo produces a robust solution for weather monitoring. This is consumer-grade but suitable for businesses to monitor the weather at any location they choose. The principles applied with Netatmo would work equally well with other cloud-based IoT solutions, whether they’re for weather or another IoT sensor.
The result is that you can see the weather information for that location in opCharts and NMIS and include it in any dashboards you require.
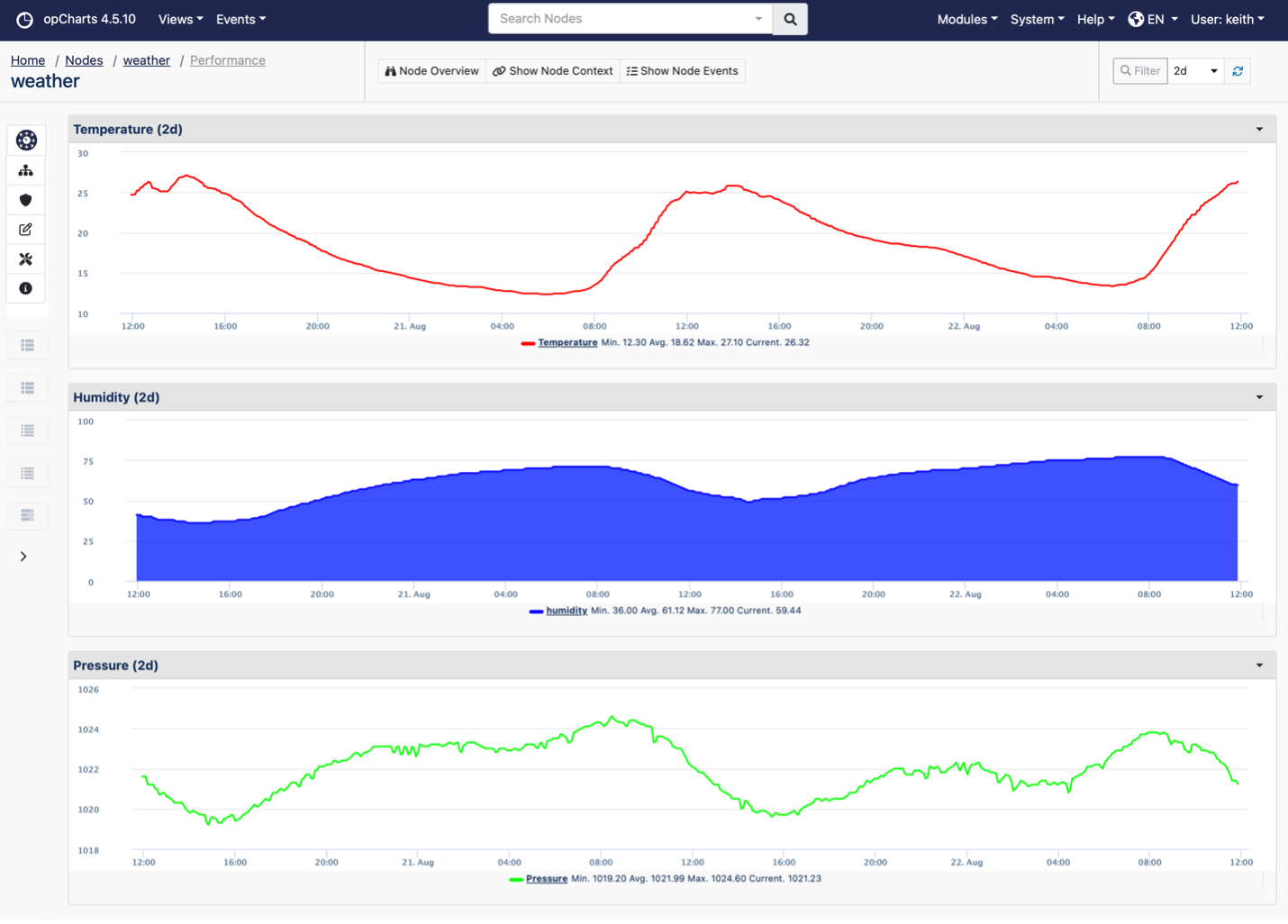
The flow of data is that the sensor collects the weather data and uploads it to the Netatmo servers on their backend. NMIS then polls the Netatmo API periodically to collect the needed weather metrics.
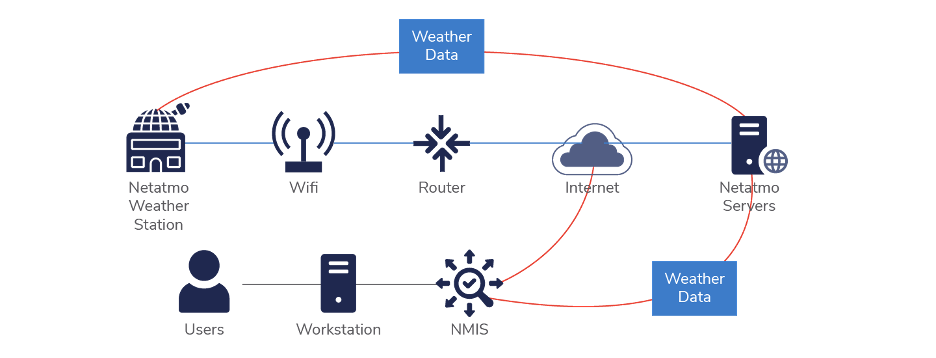
Once you sign up for a Netatmo developer account, you can create your credentials and API keys, then set up a model and plugin to collect the data. The flow of data in NMIS looks like this:

The Netatmo plugin is available on GitHub.
The Netatmo plugin provides an example of how to structure your model and plugin, including necessary configuration information. This example uses an IoT over IP system, but this method would work equally well with:
- IoT over mobile
- IoT over low energy network
With this example, you should be able to create your own plugin to talk to an IoT over IP device. Equally, the FirstWave team would be happy to assist you in getting visibility of your IoT system.
Network Devices with Controllers or Element Managers
There are many products available now that connect to the IP network and may be locally managed, but the technology solution includes a controller. Examples include:
- Wireless access points
- SDN WAN Routers
- Other SDN solutions
- Transmission networks with Element managers
While we don’t consider these technologies IoT, they work similarly. Depending on the technology, the solution would be like Smart IoT or IoT over IP, while transmission networks using Element managers would be like IoT over mobile.
NMIS already includes support for many vendors like these. For more information, contact your FirstWave representative.
Wrapping up
Now we have some definitions for the types of IoT applications and how we can communicate with the application.
Establish which type of IoT application it is:
- Smart IoT
- IoT over IP
- IoT over mobile
- IoT over low energy network
Then we determine how we can collect the data:
- Bi-directional comms
- Direct Polling
- Application Polling
- Events or Messaging
With this information, when we need to monitor an IoT application, we can classify it, understand what’s involved in getting NMIS to collect the data, and make it happen.
Learn More
To find more information about the various features and capabilities in NMIS relevant to what has been discussed, check out the following pages: