What is Distributed Network Management? Key Benefits, Challenges and Solutions for Businesses
In the digital age, the question “What is distributed network management?” has become increasingly relevant. As businesses expand their networks across multiple locations, the traditional centralized approach is giving way to a more decentralized model.
Distributed network management decentralizes control across various core points, offering enhanced efficiency and robust protection against system disruptions. This shift not only addresses the growing complexities of modern networks but also paves the way for a more resilient infrastructure.
In this article, we’ll unravel the intricacies of distributed network management, exploring its benefits, challenges, and strategies to optimize its advantages. Dive in to discover the future of network management.
The Basics of Distributed Network Management
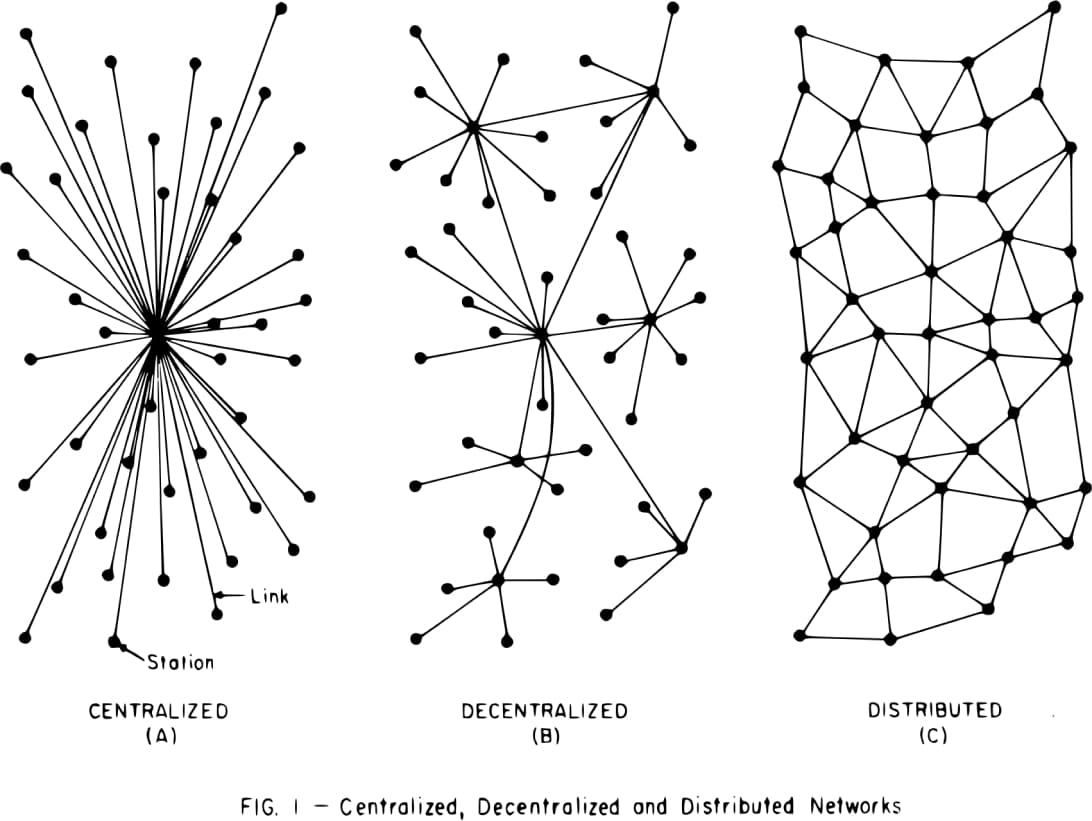
Distributed network management is the shift from relying on a central server or centralized networks to a decentralized network architecture. This means control is spread across multiple core locations, rather than being concentrated in a single central server.
Key Concepts:
- Decentralization: Distributing control across different systems, ensuring no single point of failure.
- Redundancy: Multiple points of control, so if one system or server fails, others can ensure uninterrupted services.
- Scalability: The ability to expand and accommodate growing network resources without being time-consuming.
When compared to centralized networks, where a single Network Operations Center (NOC) or central server acts as the main hub, distributed networking offers more flexibility and resilience.
| Management Type | Central Server | Resilience | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized | Yes | Low | Moderate |
| Distributed | No | High | High |
The Structure of Distributed Networks
Distributed network management focuses on how computer administrators monitor and manage network traffic. While many traditional systems depended on a single central server or NOC, this centralized approach has its limitations:
- Single Point of Failure: If the central location or NOC faces issues, the entire distributed network can be compromised.
- Limited Scalability: As the number of network resources and users grows, one system or a single central server might struggle with the load.
- Reduced Opportunities: Centralized architectures often mean fewer opportunities for diverse professionals in branch offices or customer networks.
Distributed Network Management Solutions:
- Multiple NOCs/Data Centers: Establishing several server clusters to distribute the load.
- Decentralized Control: While there might be a primary NOC or central location, other systems can operate independently.
- Redundancy: Using automated backup systems to ensure data integrity across the network.

Geographical Implications and Time Zones
Geography is crucial when considering a decentralized network for an enterprise. As organizations expand globally, they face challenges:
- Time Zone Differences: An organization with operations in the US and Asia might face network traffic peaks at different times.
- Physical Distance: Longer distances between data centers can introduce latency.
Solutions with Distributed Network Management:
- Multiple Operations Centers: By having centers in different time zones, enterprises can ensure 24/7 monitoring.
- Localized Control: This allows branch offices to manage their individual network, ensuring prompt responses based on local conditions.
In essence, distributed network management, with its focus on decentralized network architecture and distributed architecture, is not just a technical solution. It’s a strategic approach for global business operations, ensuring efficiency, resilience, and adaptability in our interconnected world.
Distributed vs. Centralized Networks
In the world of network architectures, the terms “distributed” and “centralized” are often juxtaposed, but they signify distinct concepts.
Key Differences:
- Central Control System: Distributed networks typically have a central control system, while centralized networks rely heavily on a singular control point for the entire network.
- Operational Efficiency: The presence of central control in distributed networks can boost operational efficiency, ensuring streamlined configuration management and decision-making.
- Network Nodes: In centralized networks, each node might be dependent on the main server, whereas, in distributed networks, nodes might have different levels of authority.
| Network Type | Central Control | Node Independence | Operational Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distributed | Yes | Varies | High |
| Centralized | No | High | Varies |
Challenges with Monitoring Distributed Networks
Distributed networks, while offering a range of advantages, also come with their set of monitoring challenges, especially as they encompass the entire network.
Common Challenges:
- Device Discovery: As the entire network expands, integrating new devices, especially across different locations with varied configurations, becomes intricate.
- Network Documentation: Maintaining current records of network configurations, statuses, and frequent changes is crucial.
- Visualization: Accurately representing the physical and logical layout of the local network is vital for decision-making. This becomes even more challenging when the network spans multiple locations.
- Scalability: Given that distributed networks are designed to scale, monitoring tools should be adept at handling increased loads, ensuring effective load balancing without manual reconfigurations.
Potential Solutions:
- Automated Discovery Tools: Tools that seamlessly connect and integrate new servers into the monitoring system.
- Dynamic Configuration Management Software: Tools that auto-update network configurations based on real-time changes.
- Advanced Visualization Tools: Software capable of generating real-time network maps, considering the intricacies of distributed networks.
- Intelligent Event Correlation: Utilizing advanced event management processes to better understand the true impact of incidents on service delivery, focusing efforts on highest impact tasks.
Advantages of Distributed Network Architecture
Beyond challenges, distributed network architectures offer numerous benefits that can greatly amplify an organization’s operational capabilities.
Key Benefits:
- Scalability: Distributed networks can effortlessly support growth, making them perfect for businesses on the rise.
- Resilience: The presence of multiple nodes and control points diminishes the risk of a complete system breakdown. If one server encounters issues, other servers can take over.
- Efficiency: Load balancing ensures no single server is overburdened, resulting in efficient operations.
- Geographical Reach: Distributed networks can connect across nations or even continents, apt for global operations.

Real-world Example:
Imagine a global e-commerce enterprise. During high shopping seasons, the demand for servers might surge. A distributed network ensures balanced server loads, avoiding potential crashes. If a server in the US encounters problems, the system can redirect user requests to other servers, perhaps in Europe, guaranteeing continuous service. This global distribution not only offers resilience but also optimal performance for users worldwide.
While managing distributed networks poses certain challenges, the myriad benefits they provide render them indispensable for contemporary, visionary organizations.
Challenges and Solutions for MSPs in Distributed Network Monitoring
Managed Service Providers (MSPs) face distinct challenges when it comes to distributed network monitoring. They often oversee networks for multiple clients, each presenting its unique set of requirements and configurations.
MSP-Specific Challenges:
- Varying Requirements: Different clients may have unique performance, security policies, and uptime requirements.
- Lack of Standardization: Given the multitude of clients, there’s a significant likelihood of encountering varied network devices, topologies, and protocols in the distributed network architecture.
- Isolation Needs: To prevent potential security breaches, MSPs must ensure that each client’s decentralized network remains isolated from others.
Solutions:
- Customized Monitoring Profiles: MSPs can develop specific network monitoring profiles tailored to each client, ensuring their distinct needs are addressed.
- Unified Dashboard: A centralized network dashboard can offer an overview of all client networks, while also providing detailed insights into each individual network.
- Strict Access Controls: By implementing stringent access controls, MSPs can ensure that only authorized personnel access specific client networks.

The Future of Distributed Network Monitoring and Management
As the technological landscape shifts, the strategies and tools associated with distributed network monitoring and management will also transform. Here’s a peek into what lies ahead:
Predicted Trends:
- AI-Powered Network Monitoring: Artificial Intelligence will be instrumental in preemptively identifying potential issues in decentralized networks before they escalate.
- Enhanced Security Protocols: As cyber threats grow in complexity, distributed network architecture will integrate advanced security measures to protect data.
- Integration with IoT: With the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), distributed networks will be tasked with supporting an increasing number of connected devices.
Potential Innovations:
- Self-Healing Networks: These are networks that can autonomously identify and resolve issues, eliminating the need for human intervention.
- Advanced Threat Detection: The integration of machine learning will enable real-time threat detection and neutralization.
- Seamless Integration with Emerging Tech: As technologies, including 5G, become more prevalent, distributed and centralized networks will adapt to harness their potential.
The domain of distributed network monitoring and management is in a state of constant flux. By keeping abreast of the latest innovations and trends, businesses can ensure their networks remain resilient, efficient, and future-ready.
Conclusion
Distributed network management stands at the forefront of modern networking, offering unparalleled flexibility, resilience, and scalability. As businesses expand and technology evolves, understanding and leveraging the intricacies of distributed networks becomes paramount. From effective monitoring strategies to anticipating future trends, staying informed is the key to harnessing the full potential of this dynamic domain.
If you’re keen to explore cutting-edge solutions tailored to your distributed network needs, don’t miss out. Book a demo with us and embark on a journey to optimize your network for the future. Your next step in network evolution awaits!